Interface AppConfig
stopOnTerminate?: boolean;
startOnBoot?: boolean;
enableHeadless?: boolean;
heartbeatInterval?: number;
schedule?: string[];
scheduleUseAlarmManager?: boolean;
notification?: NotificationConfig;
backgroundPermissionRationale?: PermissionRationale;
preventSuspend?: boolean;
}
Properties
Optionalstop
Controls whether to continue location-tracking after the application is terminated.
Defaults to true.
When the user terminates the app, the plugin will call stop(),
ending tracking.
Set AppConfig.stopOnTerminate to false to continue tracking after the app is terminated.
If you do configure stopOnTerminate: false, your application will terminate immediately when the user swipes it away.
However, Android and iOS behave very differently after termination:
iOS
Before an iOS app terminates, the SDK creates a stationary geofence of
GeoConfig.stationaryRadius meters around the last known position.
When the user moves beyond this stationary geofence (typically ~200 meters), iOS will
fully relaunch your application in the background, and tracking will automatically resume.
This works even after device reboot because geofences are monitored entirely by iOS at the OS level.
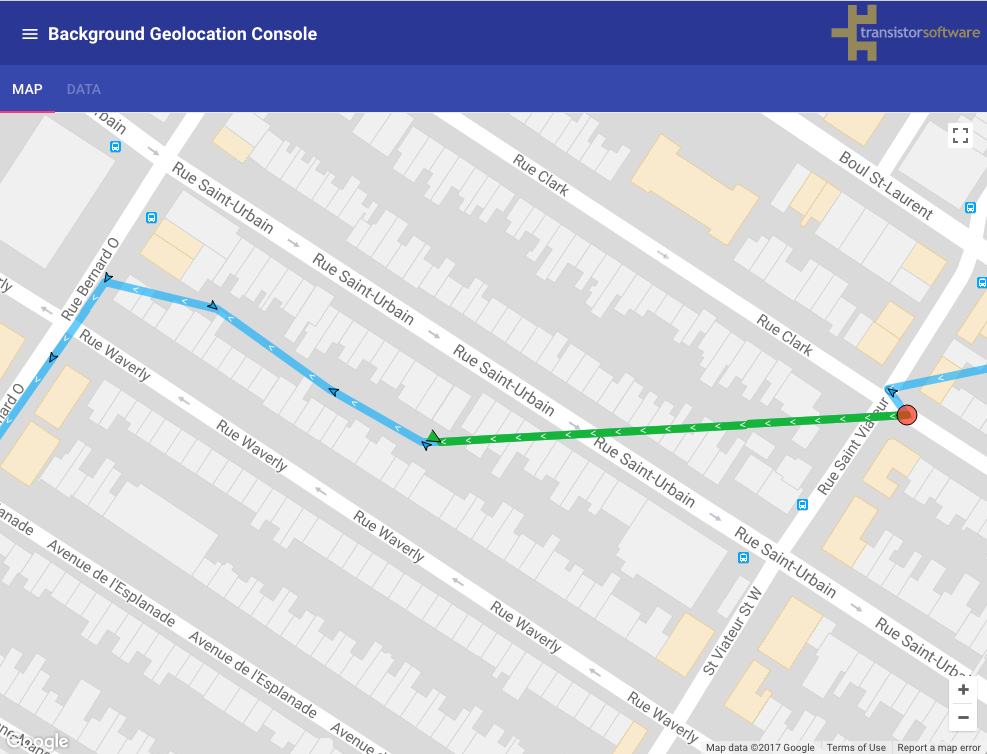
In the illustration below, imagine the user terminated the application at the red circle on the right.
As soon as the device moves ~200 meters, exiting the stationary geofence, iOS re-launches the app
and the SDK resumes tracking.
ℹ️ Demo video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aR6r8qV1TI8&t=214s
Android
Unlike iOS, Android does not pause tracking when the user terminates the app.
The native background service continues running headlessly, even without the JS/UI process.
If relying on headless mode, you must configure HttpConfig.url so that the background service can continue posting locations to your server.
See also
Optionalstart
Controls whether to resume location-tracking after the device is rebooted.
Defaults to false.
Set AppConfig.startOnBoot to true to automatically re-engage background tracking
after a device restart.
iOS
iOS cannot immediately begin tracking after a device reboot. Similar to AppConfig.stopOnTerminate: false, iOS will not relaunch your app until:
- The device moves beyond the stationary geofence created around the last known location, or
- A system Background Fetch event fires (typically every ~15 minutes), which can also restart your app.
Android
When AppConfig.startOnBoot is true, Android will automatically relaunch the SDK’s
background service after reboot (and initial device unlock).
If AppConfig.enableHeadless is also true, tracking will resume even if the JS/UI layer
has not yet started.
See also
Optionalenable
[Android only] Enables "Headless" operation allowing you to respond to events after you app has been terminated with [[stopOnTerminate]] false.
Defaults to false. In this Android terminated state, where only the plugin's foreground-service remains running, you can respond to all the plugin's events with your own callback. For more information, see [[BackgroundGeolocation.registerHeadlessTask]].
ℹ️ Note:
- Requires AppConfig.stopOnTerminate
false. - If you've configured AppConfig.stopOnTerminate
false, BackgroundGeolocation will continue to record locations (and post them to your configured HttpConfig.url) regardless ofenabledHeadless: true. You should enable this option only if you wish to perform some custom work during the headless state (for example, posting a local notification).
+ℹ️ See also:
Optionalheartbeat
Controls the rate (in seconds) at which BackgroundGeolocation.onHeartbeat
events will fire.
⚠️ Warning
- On iOS, BackgroundGeolocation.onHeartbeat will fire only when AppConfig.preventSuspend is set to
true. - On Android, the minimum interval is 60 seconds.
- It is not possible to configure a
heartbeatIntervalfaster than 60 seconds.
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
app: {
preventSuspend: true,
heartbeatInterval: 60
}
});
BackgroundGeolocation.onHeartbeat((event) => {
console.log("[onHeartbeat]", event);
// Optionally request a new location during heartbeat.
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition({
samples: 1,
persist: true
}).then((location) => {
console.log("[getCurrentPosition]", location);
});
});
ℹ️ See also
Optionalschedule
Example
"{DAY(s)} {START_TIME}-{END_TIME}"
- Times are in 24h format.
DAYuses Locale.US numbering: Sunday = 1, Saturday = 7.- You may provide:
- a single day:
"1" - a comma-separated list:
"2,4,6" - a range:
"2-6"
- a single day:
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
app: {
schedule: [
"1 17:30-21:00", // Sunday: 5:30pm–9pm
"2-6 09:00-17:00", // Mon–Fri: 9am–5pm
"2,4,6 20:00-00:00", // Mon, Wed, Fri: 8pm–midnight
"7 10:00-19:00" // Saturday: 10am–7pm
]
}
}).then((state) => {
// Start the Scheduler
BackgroundGeolocation.startSchedule();
});
// Listen for schedule state changes
BackgroundGeolocation.onSchedule((state) => {
console.log("[onSchedule] enabled?", state.enabled);
});
// Later (e.g., user logout)
BackgroundGeolocation.stopSchedule();
BackgroundGeolocation.stop(); // if tracking is currently enabled
// Modify schedule using setConfig
BackgroundGeolocation.setConfig({
app: {
schedule: [
"1-7 09:00-10:00",
"1-7 11:00-12:00",
"1-7 13:00-14:00",
"1-7 15:00-16:00",
"1-7 17:00-18:00",
"2,4,6 19:00-22:00"
]
}
});
Literal Dates
The schedule may use literal date ranges.
"yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm-HH:mm"
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
app: {
schedule: [
"2018-01-01 09:00-17:00"
]
}
});
Or specify distinct start and stop dates:
"yyyy-mm-dd-HH:mm yyyy-mm-dd-HH:mm"
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
app: {
schedule: [
"2018-01-01-09:00 2019-01-01-17:00" // track for 1 year
]
}
});
Scheduling Geofences-Only vs Location + Geofences
Append geofence or location to explicitly choose a tracking mode:
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
app: {
schedule: [
"1-7 09:00-17:00 location",
"1-7 18:00-12:00 geofence"
]
}
Since location is the default mode, it may be omitted:
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
app: {
schedule: [
"1-7 09:00-17:00 location",
"1-7 18:00-12:00 geofence"
]
}
});
Since location is the default mode, it may be omitted:
"1-7 13:00-14:00 geofence"
iOS
- iOS cannot evaluate the schedule exactly at the configured time. Evaluation occurs only when the app is awakened.
- When in a scheduled off period, iOS continues monitoring low-power
Significant Location Changes (SLC).
This guarantees periodic evaluation, especially when
{@link AppConfig.stopOnTerminate}isfalseand the OS halts traditional Background Fetch. - Schedule evaluation occurs when:
- the app pauses/resumes,
- any location is recorded (including SLC),
- a Background Fetch event fires.
Android
- Uses
AlarmManager.setExactAndAllowWhileIdle, typically evaluating on-the-minute.
ℹ️ See also
Optionalschedule
Android only Force the Android scheduler to use AlarmManager (more precise) instead of JobScheduler. Defaults to false.
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
app: {
schedule: ["1-7 09:00-17:00"],
scheduleUseAlarmManager: true
}
});
Optionalnotification
[Android only] Configures the persistent foreground-service [[Notification]] required by Android.
See NotificationConfig for detailed usage.
Optionalbackground
(Android 11+) Configures the dialog shown when requesting Always location permission on Android 11+.
Android 11 changed location authorization behavior and removed the
“Allow all the time” button from the system permission dialog.
Instead, apps may present a custom rationale dialog explaining why background
access is required. Selecting the dialog’s positiveAction sends the user
directly to the system Location Permissions screen, where they must
explicitly enable Allow all the time.
This SDK shows that dialog automatically when you have supplied AppConfig.backgroundPermissionRationale.

- Android will show the rationale dialog only once. After the user presses
the
positiveAction, it will not appear again.
(Pressing Cancel does not count.) - If the user later resets your app’s Location Permission to Ask every time, the rationale dialog may be presented again.


Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: {
locationAuthorizationRequest: 'Always'
},
app: {
backgroundPermissionRationale: {
title: "Allow {applicationName} to access this device's location in the background?",
message: "To track your activity in the background, please enable {backgroundPermissionOptionLabel} location permission.",
positiveAction: "Change to {backgroundPermissionOptionLabel}",
negativeAction: "Cancel"
}
}
});
Template Tags
You may embed the following template variables inside PermissionRationale fields, wrapped as {tagName}:
| Template Tag | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
{backgroundPermissionOptionLabel} |
Allow all the time | To track your activity in the background, please enable {backgroundPermissionOptionLabel} location permission. |
{applicationName} |
Your app name | From AndroidManifest.xml |
See also
Optionalprevent
iOS only — Prevent iOS from suspending your application after location-services have been turned off while running in the background.
Defaults to false.
Set true to keep your application alive in the background even after iOS
disables location-services. This is required when using a
heartbeat interval.
⚠️ Warning
-
preventSuspend: trueshould be used only for very specific use-cases.
It has a large and noticeable impact on battery consumption. -
You should enable
preventSuspendonly for controlled periods of time.
It is not suitable for continuous 24/7 operation. -
When the device is unplugged with the screen off, iOS still throttles BackgroundGeolocation.onHeartbeat about 2 minutes after entering the background.
Heartbeats resume immediately if:
- the screen turns on, or
- even the slightest device-motion is detected.
Application & lifecycle configuration.
AppConfiggroups options that control how the SDK integrates with your app’s lifecycle: start/stop behavior on terminate and reboot, headless/background behavior, periodic heartbeats, scheduler windows, foreground notifications, and the Android background-permission rationale dialog.Use this class via Config.app.
What belongs in
AppConfig?Platform notes
iOS
false, the SDK creates a stationary geofence and iOS will relaunch your app in the background when the device exits that region.Android
true, the native background-service continues working even after the JS/UI process is killed. Pair this with HttpConfig.url to ensure continuous uploads.AlarmManagerby default; control this with AppConfig.scheduleUseAlarmManager.Example
Configure once at startup:
Update later at runtime:
Migration from legacy
ConfigpropertiesThe following legacy properties are deprecated on Config and should now be supplied via
Config.app:Config.stopOnTerminateConfig.startOnBootConfig.enableHeadlessConfig.heartbeatIntervalConfig.scheduleConfig.scheduleUseAlarmManagerConfig.notificationConfig.backgroundPermissionRationaleConfig.preventSuspend