Interface GeoConfig
desiredAccuracy?: DesiredAccuracy;
activityType?: ActivityType;
distanceFilter?: number;
stationaryRadius?: number;
stopTimeout?: number;
stopOnStationary?: boolean;
pausesLocationUpdatesAutomatically?: boolean;
disableElasticity?: boolean;
elasticityMultiplier?: number;
stopAfterElapsedMinutes?: number;
useSignificantChangesOnly?: boolean;
disableLocationAuthorizationAlert?: boolean;
locationAuthorizationRequest?: "Always" | "WhenInUse" | "Any";
locationAuthorizationAlert?: Record<string, any>;
showsBackgroundLocationIndicator?: boolean;
locationUpdateInterval?: number;
fastestLocationUpdateInterval?: number;
deferTime?: number;
allowIdenticalLocations?: boolean;
geofenceProximityRadius?: number;
geofenceModeHighAccuracy?: boolean;
disableStopDetection?: boolean;
geofenceInitialTriggerEntry?: boolean;
filter?: LocationFilter;
enableTimestampMeta?: boolean;
}
Index
Geolocation
Other
Geolocation
Optionalactivity
[iOS only] Specifies the Core Motion activity type used by iOS to
optimize its internal stop-detection algorithm.
Apple is intentionally vague about how this affects motion interpretation, but each activity type provides platform hints about the expected movement pattern (e.g., automotive navigation, fitness, airborne).
Available values are defined as constants on ActivityType.
| Name |
|---|
| ActivityType.Other |
| ActivityType.AutomotiveNavigation |
| ActivityType.Fitness |
| ActivityType.OtherNavigation |
| ActivityType.Airborne |
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: {
activityType: ActivityType.Other,
},
});
Note: For more details, see Apple docs:
https://developer.apple.com/reference/corelocation/cllocationmanager/1620567-activitytype
Other
Optionaldesired
Specify the desired-accuracy of the geolocation system.
The following constants are defined upon the BackgroundGeolocation class:
| Name | Location Providers | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DesiredAccuracy.Navigation | (iOS only) GPS + Wifi + Cellular | Highest power; highest accuracy |
| DesiredAccuracy.High | GPS + Wifi + Cellular | Highest power; highest accuracy |
| DesiredAccuracy.Medium | Wifi + Cellular | Medium power; Medium accuracy; |
| DesiredAccuracy.Low | Wifi (low power) + Cellular | Lower power; No GPS |
| DesiredAccuracy.VeryLow | Cellular only | Lowest power; lowest accuracy |
| DesiredAccuracy.Lowest | (iOS only) | Lowest power; lowest accuracy |
⚠️ Note:
- Only
DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGHuses GPS.speed,headingandaltitudeare available only from GPS.
Optionaldistance
The minimum distance (measured in meters) a device must move horizontally before an update event is generated.
However, by default, distanceFilter is elastically auto-calculated by the plugin: When speed increases, distanceFilter increases; when speed decreases, so too does distanceFilter.
ℹ️ Note:
- To disable this behavior, configure disableElasticity
true. - To control the scale of the automatic
distanceFiltercalculation, see {elasticityMultiplier
distanceFilter is auto-scaled by rounding speed to the nearest 5 m/s and adding distanceFilter meters for each 5 m/s increment.
For example, at biking speed of 7.7 m/s with a configured distanceFilter: 30:
Example
rounded_speed = round(7.7, 5)
=> 10
multiplier = rounded_speed / 5
=> 10 / 5 = 2
adjusted_distance_filter = multiplier * distanceFilter
=> 2 * 30 = 60 meters
At highway speed of 27 m/s with a configured distanceFilter: 50:
Example
rounded_speed = round(27, 5)
=> 30
multiplier = rounded_speed / 5
=> 30 / 5 = 6
adjusted_distance_filter = multiplier * distanceFilter * elasticityMultipiler
=> 6 * 50 = 300 meters
Note the following real example of "elasticity" on highway 101 towards San Francisco as the driver slows down while running into
slower traffic — locations become compressed as distanceFilter decreases.
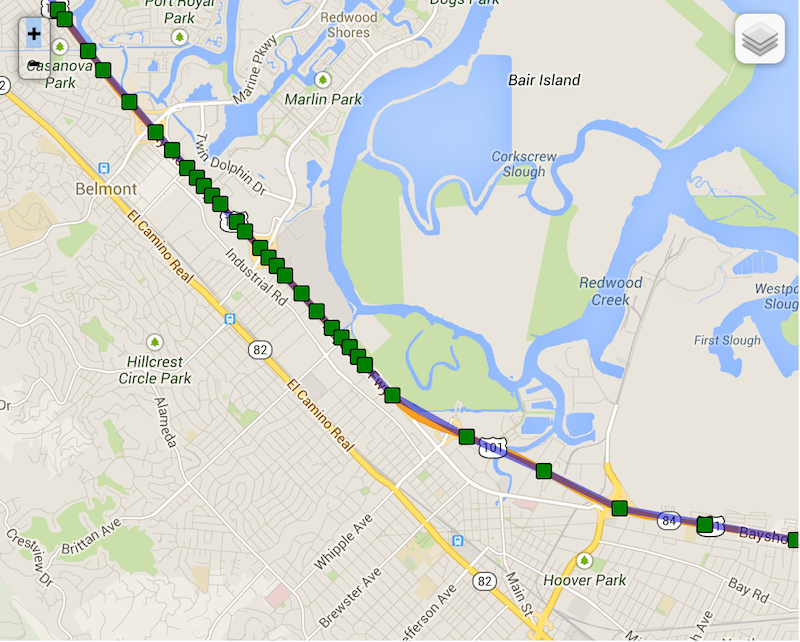
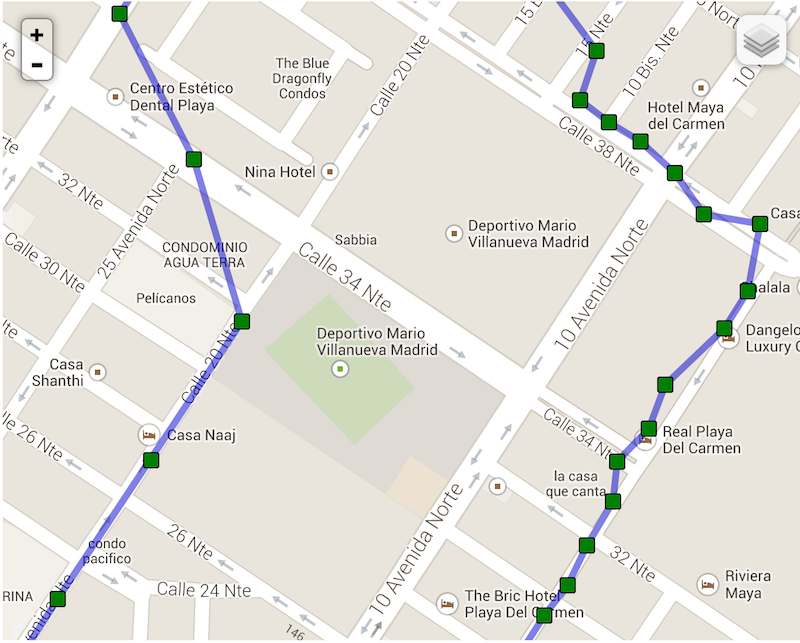
Compare now background-geolocation in the scope of a city. In this image, the left-hand track is from a cab-ride, while the right-hand track is walking speed.
Optionalstationary
The minimum distance the device must move beyond the stationary location for aggressive background-tracking to engage.
⚠️ Note: The device will not detect the exact moment it moves out of the stationary-radius. In normal conditions, it will typically take ~200 meters of movement before the plugin begins tracking.
Configuring stationaryRadius: 0 has NO EFFECT. In fact the plugin enforces a minimum stationaryRadius of 25 and
in-practice, the native API won't respond for at least 200 meters.
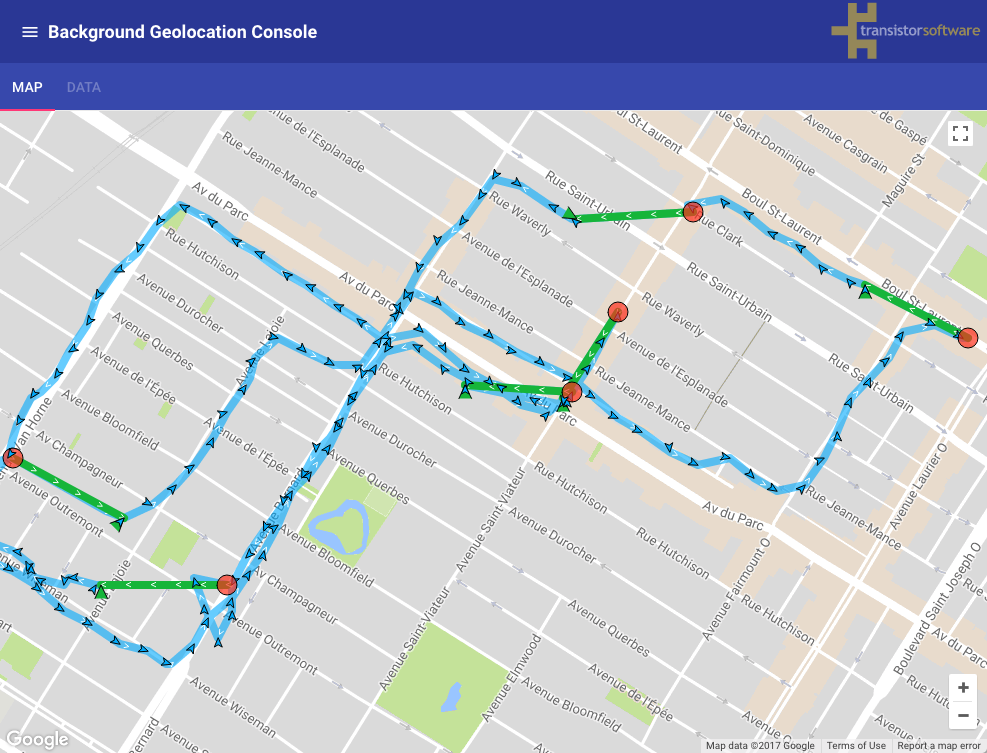
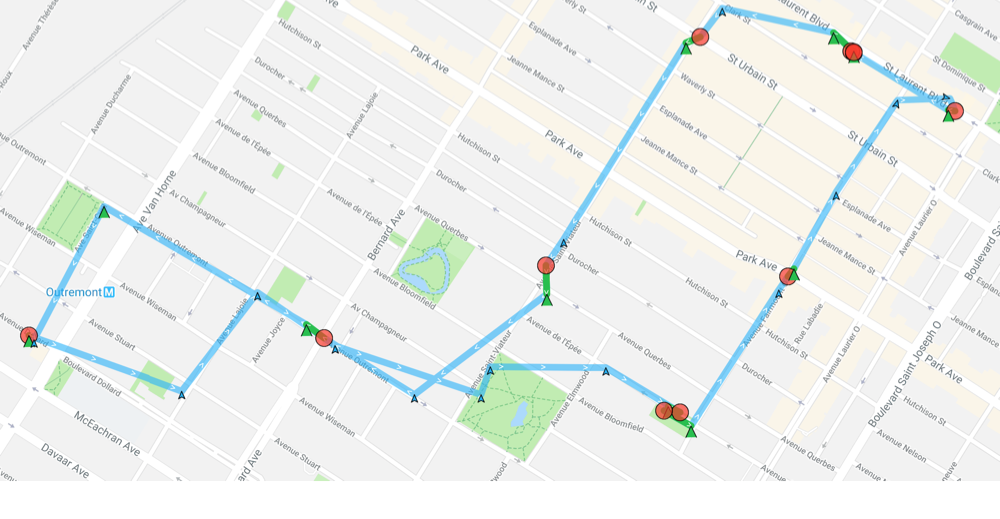
The following image shows the typical distance iOS requires to detect exit of the stationaryRadius:
- Green polylines: represent a transition from stationary state to moving (~200 meters).
- Red circles: locations where the plugin entered the stationary state.
ℹ️ See also:
Optionalstop
Minutes to wait in moving state with no movement before considering the device stationary.
Defaults to 5 minutes. When in the moving state, specifies the number of minutes to wait before turning off location-services and
transitioning to stationary state after the ActivityRecognition System detects the device is STILL. An example use-case for this
configuration is to delay GPS OFF while in a car waiting at a traffic light.
:warning: Setting a very long stopTimeout will cause the device's location API to remain ON while the device is potentially motionless for extended periods, which may have a significant impact on battery life. It depends upon your use-case.
ℹ️ See also:
Optionalstop
Automatically BackgroundGeolocation.stop when the stopTimeout elapses.
The plugin can optionally automatically stop tracking when the stopTimeout timer elapses. For example, when the plugin first fires BackgroundGeolocation.onMotionChange into the moving state, the next time an onMotionChange event occurs into the stationary state, the plugin will have automatically called BackgroundGeolocation.stop upon itself.
⚠️ stopOnStationary will only occur due to stopTimeout timer elapse. It will not occur by manually executing
BackgroundGeolocation.changePace false.
Optionalpauses
[iOS only] Prevent the iOS location API from ever automatically turning off.
⚠️ WARNING:
This option should almost always remain undefined.
Only set this if you know exactly what you're doing.
By default, the SDK automatically turns off iOS location-services when the device remains stationary for stopTimeout minutes.
When this option is explicitly set to false, location-services will never
be turned off. In this mode:
- ActivityConfig.disableStopDetection will automatically be forced to
true - You are responsible for disabling tracking when you no longer need it
- This can have severe battery-drain implications
- AppConfig.preventSuspend will no longer function
This option exists only for highly specialized use-cases and should generally not be used in production applications.
Optionaldisable
Defaults to false. Set true to disable automatic, speed-based distanceFilter auto-scaling. By default, the SDK automatically
increases distanceFilter as speed increases (and decreases it as speed decreases) in order to record fewer locations and conserve energy.
Note the following real example of "elasticity" on highway 101 towards San Francisco as the driver slows down while running into slower traffic — locations become compressed as distanceFilter decreases.

ℹ️ See also:
Optionalelasticity
Controls the scale of automatic speed-based distanceFilter elasticity.
Increasing elasticityMultiplier will result in fewer location samples as speed increases. A value of 0 has the same effect as
disableElasticity true.
Optionalstop
Automatically BackgroundGeolocation.stop tracking after x minutes.
The plugin can optionally automatically BackgroundGeolocation.stop after some number of minutes elapses after the BackgroundGeolocation.start method was called.
Optionaluse
Set true in order to disable constant background-tracking. Locations will be recorded only periodically.
Defaults to false. A location will be recorded only every 500 to 1000 meters (can be higher in non urban environments; depends upon the spacing of Cellular towers). Many of the plugin's configuration parameters will have no effect, such as distanceFilter, stationaryRadius, activityType, etc.
Using significantChangesOnly: true will provide significant power-saving at the expense of fewer recorded locations.
iOS
Engages the iOS Significant Location Changes API API for only periodic location updates every 500-1000 meters.
⚠️ If Apple has rejected your application, refusing to grant your app the privilege of using the UIBackgroundMode: "location", this can be a solution.
Android
A location will be recorded several times per hour while the device is in the moving state. No foreground-service will be run (nor its corresponding persistent NotificationConfig).
Example 1 useSignificantChangesOnly: true
Example 2 useSignificantChangesOnly: false (Default)
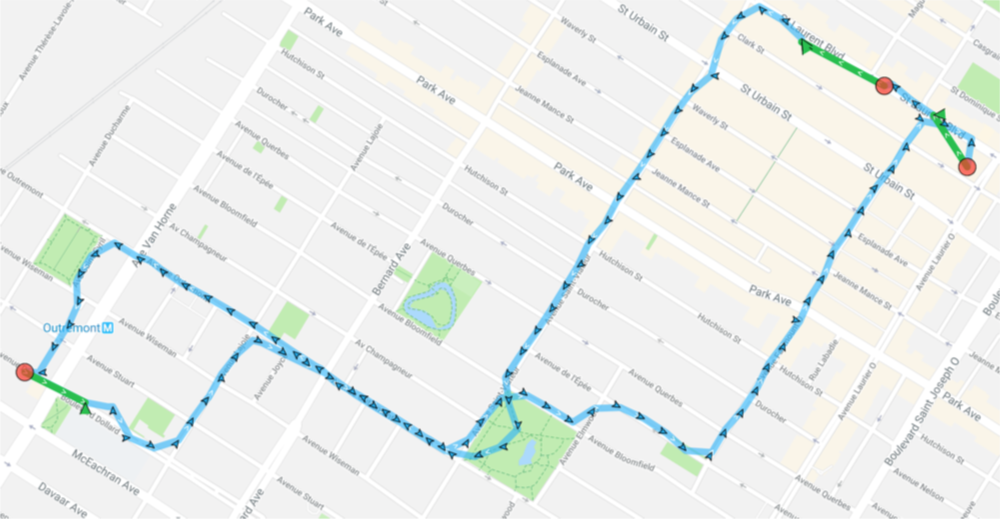
Optionaldisable
Disables automatic authorization alert when plugin detects the user has disabled location authorization.
You will be responsible for handling disabled location authorization by listening to the BackgroundGeolocation.onProviderChange event.
By default, the plugin automatically shows a native alert to the user when location-services are disabled, directing them to the settings screen. If you do not desire this automated behavior, set disableLocationAuthorizationAlert: true.
iOS
The iOS alert dialog text elements can be configured via locationAuthorizationAlert and locationAuthorizationRequest.
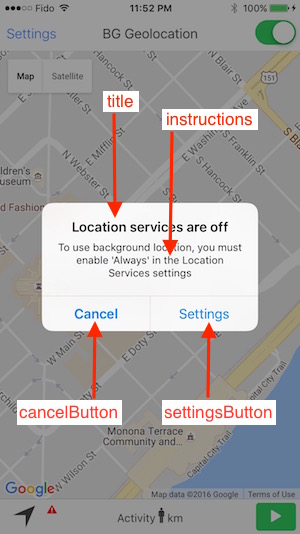
Android
Android can detect when the user has configured the device's Settings->Location in a manner that does not match your location request (eg: desiredAccuracy). For example, if the user configures Settings->Location->Mode with Battery Saving (ie: Wifi only) but you've specifically requested DesiredAccuracy.High (ie: GPS), Android will show a dialog asking the user to confirm the desired changes. If the user clicks [OK], the OS will automcatically modify the Device settings.
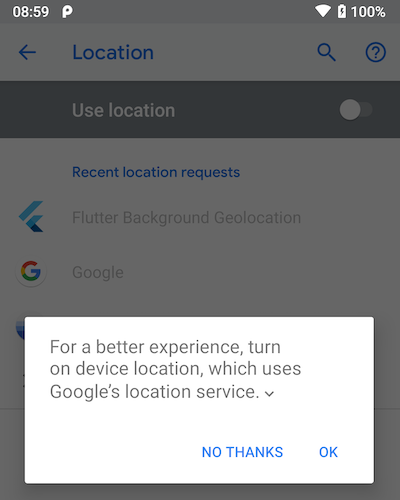
This automated Android dialog will be shown in the following cases:
Optionallocation
Defines the desired location-authorization level your app expects from the user:
"Always""WhenInUse""Any"
Defaults to "Always".
Setting locationAuthorizationRequest tells the SDK what authorization level
your app expects, so it can guide the user and present helpful upgrade dialogs
when needed. If you do not care which authorization is granted, configure
"Any".
If you request "Always" but the user grants only When-In-Use, the SDK
will display locationAuthorizationAlert unless disabled via
disableLocationAuthorizationAlert.
iOS
iOS 13 introduced major changes to the authorization workflow.
Apps no longer receive Always Allow on the initial dialog.
After a user first grants While Using the App, iOS may show a second, system-managed upgrade prompt, asking if they’d like to enable:
- Keep Only While Using
- Change to Always Allow
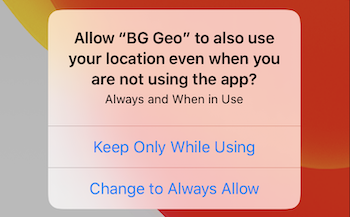
1. When locationAuthorizationRequest: "Always"
The user will first see the While Using App dialog, followed immediately by the upgrade prompt asking for Always Allow:

If the user denies Always, the SDK displays locationAuthorizationAlert (unless disabled).

2. When locationAuthorizationRequest: "WhenInUse"
Only the initial dialog appears:
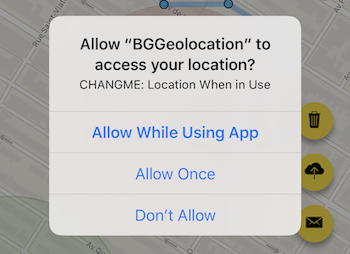
If you later upgrade the config to "Always", the upgrade prompt
appears immediately:
3. When locationAuthorizationRequest: "Any"
The SDK requests Always internally, but accepts either result. iOS may spontaneously show the upgrade dialog later:

Example
// Start with When-In-Use
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: { locationAuthorizationRequest: "WhenInUse" }
});
async function onClickStartTracking() {
await BackgroundGeolocation.start();
// Later — you may upgrade to Always at any time.
BackgroundGeolocation.setConfig({
geolocation: { locationAuthorizationRequest: "Always" }
});
}
Android
Android 11+ (targetSdkVersion ≥ 30)
Android 11 removes Allow all the time from the initial dialog.
Instead, apps must present a custom rationale UI before navigating the user
to the system Location Permissions screen.
The SDK automatically presents AppConfig.backgroundPermissionRationale when configured.
- The dialog shows only once, unless the user resets permissions.

BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: { locationAuthorizationRequest: "Always" },
app: {
backgroundPermissionRationale: {
title: "Allow access to this device's location in the background?",
message: "To track your trips, please enable 'Allow all the time' location permission.",
positiveAction: "Change to Allow all the time",
negativeAction: "Cancel"
}
}
});
1. When locationAuthorizationRequest: "Always"
After granting While Using, Android immediately displays your configured rationale dialog:

2. When locationAuthorizationRequest: "WhenInUse"
Only the initial system dialog appears:
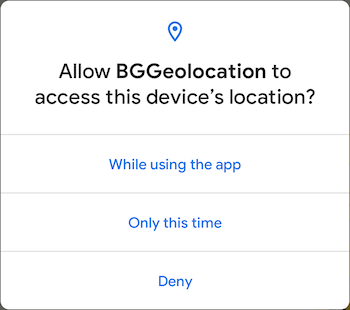
Upgrading later to "Always" triggers the rationale dialog:

3. When locationAuthorizationRequest: "Any"
Treated the same as "Always".
Optionallocation
[iOS only] Customize the text displayed in the SDK’s location-authorization alert dialog.
When locationAuthorizationRequest is configured as
"Always" or "WhenInUse" and the user subsequently downgrades or disables
location permission in iOS Settings, the SDK presents an alert directing the
user back to the Settings screen.
locationAuthorizationAlert lets you override all of the strings used in that
alert. You must supply an object matching locationAuthorizationAlert.
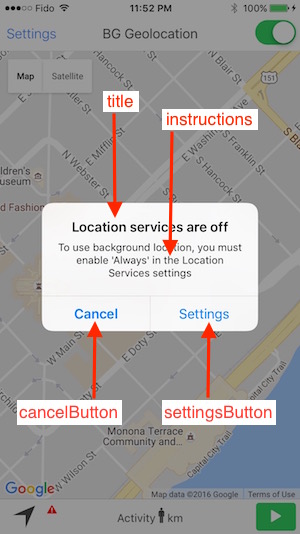
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: {
locationAuthorizationAlert: {
titleWhenNotEnabled: "Location services are not enabled",
titleWhenOff: "Location services are OFF",
instructions:
"Please enable 'Always' in Location Services to allow background tracking.",
cancelButton: "Cancel",
settingsButton: "Open Settings"
}
}
});
⚠️ Warning
If you provide locationAuthorizationAlert, you must supply all
locationAuthorizationAlert fields — not just a subset.
Optionalshows
[iOS Only] A Boolean indicating whether the status bar changes its appearance when an app uses location services in the background with Always authorization.
The default value of this property is true. The background location usage indicator is a blue bar or a blue pill in the status bar on iOS; on watchOS the indicator is a small icon. Users can tap the indicator to return to your app.
This property affects only apps that received Always authorization. When such an app moves to the background, the system uses this property to determine whether to change the status bar appearance to indicate that location services are in use. Set this value to true to maintain transparency with the user.
For apps with When In Use authorization, the system changes the appearance of the status bar when the app uses location services in the background.
Optionallocation
[Android only] Desired interval for active location updates, in milliseconds.
⚠️ Important
- To use
locationUpdateInterval, you must also set distanceFilter to0.
IfdistanceFilter> 0, it overrides this interval.
This value tells Android how frequently your app wants location updates. The system will try to honor it but may deliver updates:
- slower (no providers available),
- faster (another app requests faster updates),
- or not at all (permission or system constraints).
Apps with only coarse location permission may have this interval silently throttled.
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: {
distanceFilter: 0, // Required — otherwise this field is ignored.
locationUpdateInterval: 5000 // Request a fix every ~5 seconds
}
});
ℹ️ See also
- Android’s
LocationRequest.setInterval:
https://developers.google.com/android/reference/com/google/android/gms/location/LocationRequest.html#setInterval(long)
Optionalfastest
[Android only] Explicitly sets the fastest interval for location updates,
in milliseconds.
This value defines the maximum rate at which the SDK will deliver passive location updates. It may be faster than locationUpdateInterval when other applications or system components are triggering more frequent updates.
Configuring a faster passive rate allows your application to benefit from locations generated by other apps without increasing power usage.
Unlike locationUpdateInterval, this parameter is exact:
your application will never receive updates faster than this value.
- If not configured, the default fastest interval is 30000 ms (30 seconds).
- A value of
0is allowed but not recommended, since future devices may deliver extremely rapid updates. - If
fastestLocationUpdateIntervalis slower than locationUpdateInterval, the effective fastest interval becomes locationUpdateInterval.
Example
import BackgroundGeolocation from "react-native-background-geolocation";
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: {
// Receive passive updates as fast as 5 seconds
fastestLocationUpdateInterval: 5000,
// Active updates occur according to distanceFilter or locationUpdateInterval
}
});
See also
Optionaldefer
[Android only] Sets the maximum wait time in milliseconds for location updates.
Defaults to 0 (no defer).
If you pass a value at least 2x larger than the interval specified with locationUpdateInterval, then location delivery may be delayed and multiple locations can be delivered at once.
Locations are determined at the locationUpdateInterval rate, but can be delivered in batch after the interval you set in this method. This can consume less battery and give more accurate locations, depending on the device's hardware capabilities. You should set this value to be as large as possible for your needs if you don't need immediate location delivery.
Optionalallow
[Android only] Allow recording locations which are duplicates of the previous.
By default, the Android plugin will ignore a received location when it is identical to the previous location. Set true to override this behavior
and record every location, regardless if it is identical to the last location.
In the logs, you will see a location being ignored:
TSLocationManager: ℹ️ IGNORED: same as last location
An identical location is often generated when changing state from stationary -> moving, where a single location is first requested (the BackgroundGeolocation.onMotionChange location) before turning on regular location updates.
Changing geolocation config params can also generate a duplicate location (eg: changing distanceFilter).
Optionalgeofence
Defines the radius (in meters) around the device used to query for geofences that should be actively monitored.
The default — and minimum — value is 1000 meters.
Mobile platforms allow only a limited number of concurrently monitored geofences
(iOS: 20, Android: ~100).
The SDK removes this limitation by allowing you to register any number of geofences (thousands even). It stores them in its internal database and performs efficient spatial queries to determine which subset of geofences should be activated based on the device’s current position.
As the device moves, this radius determines when the monitored geofence set changes, firing BackgroundGeolocation.onGeofencesChange.
See also

Optionalgeofence
[Android only] Enable high-accuracy for geofence-only mode (See BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences).
⚠️ Warning: Will consume more power.
Defaults to false. Runs Android's BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences with a foreground service (along with its corresponding persistent AppConfig.notification).
Configuring geofenceModeHighAccuracy: true will make Android geofence triggering far more responsive. In this mode, the usual config options to control location-services will be applied:
- GeoConfig.desiredAccuracy (DesiredAccuracy.Medium works well).
- GeoConfig.locationUpdateInterval
- GeoConfig.distanceFilter
- GeoConfig.deferTime
With the default geofenceModeHighAccuracy: false, a device will have to move farther into a geofence before the ENTER event fires and farther out of a geofence before
the EXIT event fires.
The more aggressive you configure the location-update params above (at the cost of power consumption), the more responsive will be your geofence-triggering.
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: {
geofenceModeHighAccuracy: true,
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_MEDIUM,
locationUpdateInterval: 5000,
distanceFilter: 50,
}
}).then((state) => {
BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences();
});
Optionaldisable
Disable the motion-activity–based stop-detection system.
When enabled (true), the SDK ignores platform motion-activity signals when
determining whether the device is stationary. This affects how and when
location-services are automatically turned off on both iOS and Android.
iOS
Disables the accelerometer-based stop-detection system. When disabled, the plugin falls back to the default iOS behavior: location-services turn off automatically after exactly 15 minutes of no motion. In this mode, you lose control over stopTimeout.
To completely prevent iOS from automatically disabling location-services,
you must also set pausesLocationUpdatesAutomatically
to false:
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: {
disableStopDetection: true,
pausesLocationUpdatesAutomatically: false
}
});
⚠️ iOS location-services will never turn off!
With the configuration above, iOS will never disable location-services. This can heavily drain the battery. Do not use this unless you fully control tracking manually (for example, a workout app that toggles tracking using BackgroundGeolocation.changePace).
iOS Stop-detection timing
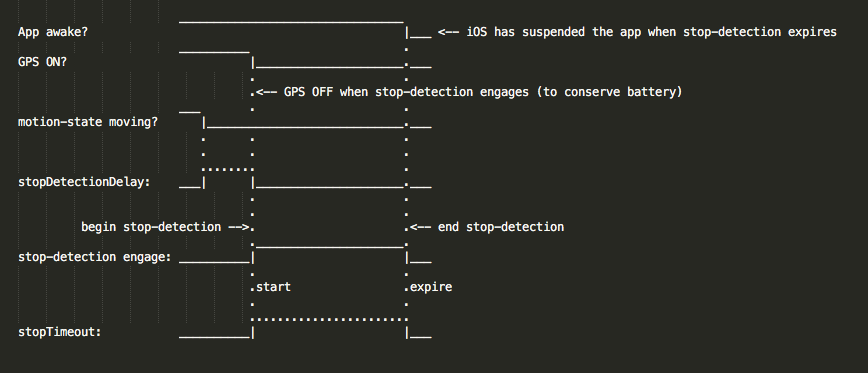
Android
If set to true, Android location-services will never turn off
automatically. It becomes your responsibility (or the user’s) to disable
tracking manually by calling:
- BackgroundGeolocation.changePace with
false, or - BackgroundGeolocation.stop
Optionalgeofence
When a device is already within a just-created geofence, fire the enter transition immediately.
Defaults to true. Set false to disable triggering a geofence immediately if device is already inside it.
ℹ️ See also
-
- 📘 [[Geofence | Geofencing Guide]].
Optionalfilter
Defines how raw GPS samples are filtered, denoised, and smoothed before being recorded or used for odometer calculations.
LocationFilter is supplied via GeoConfig.filter and provides
fine-grained control over how the SDK handles noisy or inconsistent
location data from the underlying platform.
Overview
The native platform continuously produces raw CLLocation (iOS) or
Location (Android) samples. The LocationFilter applies:
- Kalman filtering
- rolling-window averaging
- speed, distance, and accuracy constraints
These produce smoother paths, reduce jitter, and improve odometer stability.
Example
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
geolocation: {
filter: {
policy: LocationFilterPolicy.Adjust,
useKalman: true,
kalmanProfile: KalmanProfile.Default,
trackingAccuracyThreshold: 100,
odometerAccuracyThreshold: 20
}
}
});
Filtering Flow
Parameters
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| LocationFilter.policy | Selects which filtering policy to apply. See LocationFilterPolicy. |
| LocationFilter.useKalman | Enables Kalman filtering of speed and position (default: true). |
| LocationFilter.kalmanDebug | Enables verbose Kalman diagnostic logs. |
| LocationFilter.kalmanProfile | Selects a Kalman tuning profile (see KalmanProfile). |
| LocationFilter.rollingWindow | Number of samples for rolling burst averaging. Larger values increase smoothness but reduce responsiveness. |
| LocationFilter.burstWindow | Duration of each averaging burst (seconds). Default: 10. |
| LocationFilter.maxBurstDistance | Maximum distance (meters) for samples to be included in the same burst window. Default: 300. |
| LocationFilter.trackingAccuracyThreshold | Minimum GPS horizontal accuracy (meters) required to accept a location. Default: 100. |
| LocationFilter.maxImpliedSpeed | Maximum implied speed (m/s) before rejecting a sample as unrealistic. Default: 60 (~216 km/h). |
| LocationFilter.filterDebug | Enables verbose logging of filter decisions (ACCEPTED, REJECTED, etc). |
| LocationFilter.odometerUseKalmanFilter | Applies Kalman smoothing to odometer calculations. |
| LocationFilter.odometerAccuracyThreshold | Maximum accuracy (meters) allowed for a sample to affect the odometer. Default: 100. |
Notes
- Distances are in meters.
- Time fields are in milliseconds unless otherwise specified.
- Filtering affects recorded locations only; it does not influence real-time motion detection.
Disable all filtering
Optionalenable
Enable extra timestamp meta data to be appended to each recorded location, including system-time.
Some developers have reported GPS Location.timestamp issues with some Android devices. This option will append extra meta-data related to the device's system time.
Android implementation:
JSONObject timestampMeta = new JSONObject();
timestampMeta.put("time", mLocation.getTime());
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR1) {
timestampMeta.put("systemClockElaspsedRealtime", SystemClock.elapsedRealtimeNanos()/1000000);
timestampMeta.put("elapsedRealtime", mLocation.getElapsedRealtimeNanos()/1000000);
} else {
timestampMeta.put("systemTime", System.currentTimeMillis());
}
iOS Implementation:
long long systemTime = (long long)([[NSDate date] timeIntervalSince1970] * 1000.0);
long long locationTime = (long long)([_location.timestamp timeIntervalSince1970] * 1000.0);
long long uptime = (long long) [self.class uptime] * 1000;
return @{
@"time": @(locationTime),
@"systemTime": @(systemTime),
@"systemClockElapsedRealtime": @(uptime)
};
Geolocation Configuration
GeoConfig defines all geolocation-related options for the BackgroundGeolocation SDK.
These parameters control:
Overview
GeoConfig is supplied via Config.geolocation when calling BackgroundGeolocation.ready or BackgroundGeolocation.setConfig.
Example
Migration from Legacy Flat Config
Previously, geolocation options were configured directly on the root Config object:
These options now belong to this GeoConfig group:
Legacy flat fields remain supported for backward compatibility, but they are now marked deprecated. Prefer Config.geolocation going forward for clarity and structure.
See also